Aviation Law
Classification of Airspace
ATS airspace is classified and designated in accordance with the following:
Class A. IFR flights only are permitted, all flights are provided with air traffic control service and are separated from each other.
Class B. IFR and VFR flights are permitted, all flights are provided with air traffic control service and are separated from each other.
Class C. IFR and VFR flights are permitted, all flights are provided with air traffic control service and IFR flights are separated from other IFR flights and from VFR flights. VFR flights are separated from IFR flights and receive traffic information in respect of other VFR flights.
Class D. IFR and VFR flights are permitted and all flights are provided with air traffic control service, IFR flights are separated from other IFR flights and receive traffic information in respect of VFR flights, VFR flights receive traffic information in respect of all other flights.
Class E. IFR and VFR flights are permitted, IFR flights are provided with air traffic control service and are separated from other IFR flights. All flights receive traffic information as far as is practical. Class E shall not be used for control zones.
Class F. IFR and VFR flights are permitted, all participating IFR flights receive an air traffic advisory service and all flights receive flight information service if requested.
Class G. IFR and VFR flights are permitted and receive flight information service if requested.
The services provided and flight requirements for different classes of airspace are shown in the table below.
| Class | Type of Flight | Separation Provided | Service Provided | Speed Limitation | Radio Communication Requirement | Subject to ATC Clearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | IFR only | All aircraft | Air traffic control service | Not applicable | Continuous two-way | Yes |
| B | IFR | All aircraft | Air traffic control service | Not applicable | Continuous two-way | Yes |
| B | VFR | All aircraft | Air traffic control service | Not applicable | Continuous two-way | Yes |
| C | IFR | IFR from IFR, IFR from VFR | Air traffic control service | Not applicable | Continuous two-way | Yes |
| C | VFR | VFR from IFR | 1) Air traffic control service for separation from IFR 2) VFR/VFR traffic information service (and traffic avoidance advice on request) | 250 kts IAS below 10000 ft amsl | Continuous two-way | Yes |
| D (1) | IFR | IFR from IFR | Air traffic control service, traffic information about VFR flights (and traffic avoidance advice on request) | 250 kts IAS below 10000 ft amsl | Continuous two-way | Yes |
| D (1) | VFR | Nil | IFR/VFR and VFR/VFR traffic information (and traffic avoidance advice on request) | 250 kts IAS below 10000 ft amsl | Continuous two-way | Yes |
| E (2) | IFR | IFR from IFR | Air traffic control service and, as far as practical, traffic information about VFR flights | 250 kts IAS below 10000 ft amsl | Continuous two-way | Yes |
| E (2) | VFR | Nil | Traffic information as far as practical | 250 kts IAS below 10000 ft amsl | No | No |
| F | IFR | IFR from IFR as far as practical | Air traffic advisory service; flight information service | 250 kts IAS below 10000 ft amsl | Continuous two-way | No |
| F | VFR | Nil | Flight information service | 250 kts IAS below 10000 ft amsl | No | No |
| G | IFR | Nil | Flight information service | 250 kts IAS below 10000 ft amsl | Continuous two-way | No |
| G | VFR | Nil | Flight information service | 250 kts IAS below 10000 ft amsl | No | No |
Important Notes:
(1): In Class D airspace, both IFR and VFR traffic are required to follow ATC clearances; however, ATC are only responsible for IFR against IFR separation.
(2): In Class E airspace, ATC does not provide separation between IFR and VFR traffic; IFR traffic shares responsibility for separation from uncontrolled VFR traffic with that traffic.
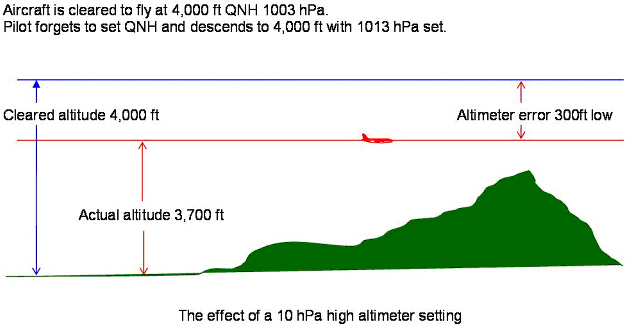
Altimeter
The aircraft altimeter barometric sub-scale must be set to the appropriate setting for the phase of flight. These are:
- Flight level. Standard pressure setting (1013 hPa) is set when flying by reference to flight levels at or above the transition level;
- Altitude. Regional or airfield pressure setting (QNH) is set when flying by reference to altitude above mean sea level at or below the transition altitude;
- Height. Altimeter pressure setting indicating height above airfield or touchdown (QFE) is set when approaching to land at airfield where this procedure is in use. Note that this setting is not used in other portions of the flight (climb, cruise and initial descent).
Aircraft are not supposed to fly level within the transition layer (between the transition altitude and the transition level). When passing through it, their vertical position is expressed in:
- flight levels during climb (i.e. above the transition altitude)
- altitudes during descent (i.e. below the transition level)
If no transition altitude and transition level are defined (which is common for en-route flights outside the TMAs), the vertical position of aircraft shall be expressed in terms of:
- flight levels at or above the lowest usable flight level
- altitudes below the lowest usable flight level
Failure to set the appropriate barometric sub-scale pressure setting may result in a significant deviation from the cleared altitude or Flight Level